With blockchain, you can imagine a world in which documents are embedded in digital code and stored in transparent, shared databases, where they are protected from deletion, tampering, and revision.
In this world, every agreement, every process, every task, and every payment would have a digital record and signature that could be identified, validated, stored, and shared.
Intermediaries like lawyers, brokers, and institutions like notaries might no longer be necessary. Individuals, organizations, and machines would freely transact and interact with one another with little friction.
This is the immense potential of blockchain.
The potential application of content decentralization and distribution is enormous: people will own their digital identity and records, creating a single, immutable, and verifiable record store. Think of all the identity or residence documents, medical records, educational or professional certificates, and licenses that this could apply to.
All these documents and their metadata can be issued, and be digitally signed using blockchain.
No more fake certifications, no more degree mills, and no more photoshopped papers!
Students, for example, may apply for further study, a job, immigration to another country. It would straightforward to prove their level of studies or knowledge of a language to attend university. Entities like recruiters, employers, government, and universities can verify the student’s credentials without relying on central authorities, in just minutes, and with no other intermediaries.
How Digital Signatures Work - Seal Your Digital Assets
An authority issues certificates (say, an education institute). These certificates are stored on a centralized document management server or a distributed file system like IPFS and signed with a cryptographic function.
The document URI, metadata, and the content hash are then encrypted and stored on the blockchain digital ledger and attached to the user’s digital identity. The system issues a unique authenticity token, which identifies the document in a non-questionable way.
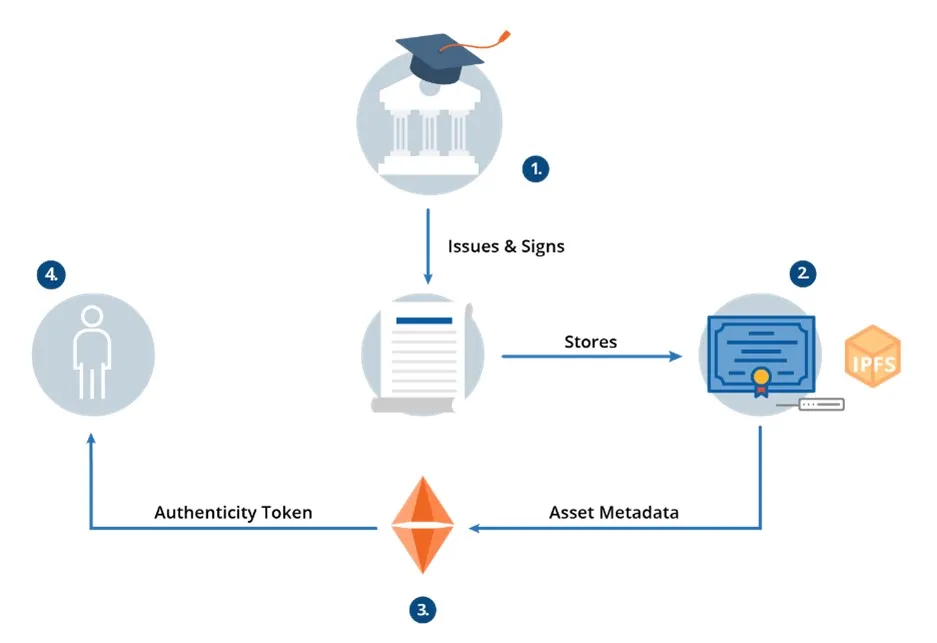
The original document data is never stored in the blockchain, only the document’s hash.
Using a distributed ledger makes the solution decentralized and provides the highest possible security, efficiency, and compliance.
If a document’s authenticity is ever questioned, the “off-chain” file can be re-hashed later and the resulting hash compared to the “on-chain” value.
If the hash values match, the document is authentic, but if anything is modified, even just a single character, the hashes will not match, making it obvious that a change has occurred.
How Digital Signatures Work - Verify Your Digital Assets
Let’s say that, at a given point, a user needs to present their certificates to a third party, like an employer. He can share the authenticity token with the third party for verification. The token works as the file’s contract address, as it contains all the necessary information to verify that the document exists and is authentic (not counterfeited).
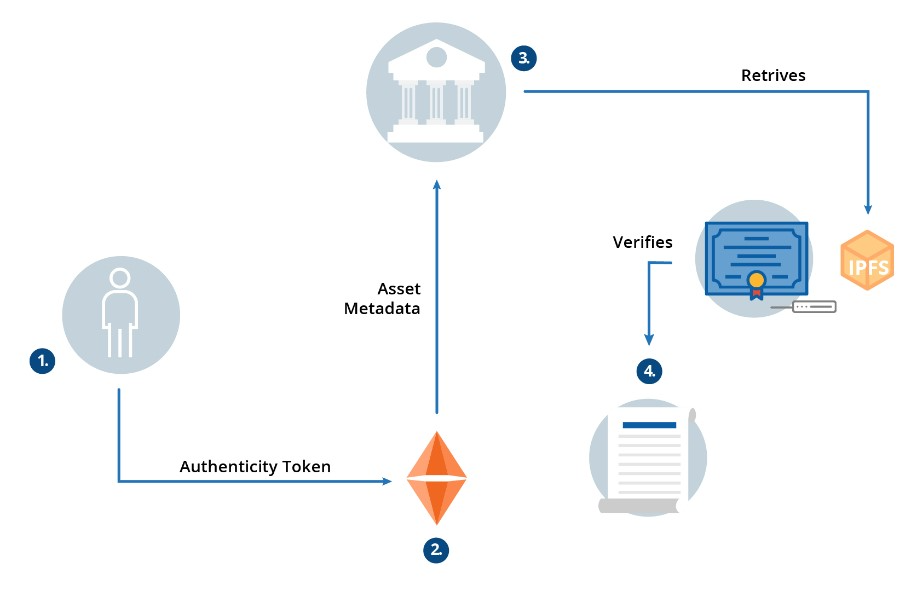
Processing documents and any unstructured data and their metadata and integrating them with blockchain creates immutable and independently verifiable records of transactions. There is now a way a proof of existence and authenticity for these digital assets.
Proof of existence refers to creating an unalterable date and time stamp for a specific object. It means that you can prove that a certain information object, like an email, document, or image, existed at a certain point in time.
Proof of authenticity asserts that an object is authentic, i.e., that it has not changed since it was stored at the indicated time instant. This is accomplished by digitally signing an object and thus creating a hash, its unique identifier. The identifier gets then committed into the distributed blockchain ledger, and the transaction gets timestamped as well.
Since every entry in the blockchain is immutable, this means that you have proof that this specific object existed at a certain point in time.
Why use Blockchain to Create a Digital Signature?
Why should we use blockchain to sign and verify digital assets when solutions for electronic signature already exist and are broadly adopted in the industry? Here is why:
- Digital signatures stored on a blockchain live independently of the object the signature refers to. There is no need for a central certificate authority or central timestamping server, which are the typical dependencies of existing e-signature systems.
- You can achieve parallel signing and independent verification, with or without the object itself.
- You no longer store digital signatures inside the document, as with traditional e-signing solutions. With the old-school solutions, whoever needed to check if a document is signed would have full read access to all the content in the document.
- By signing documents on a blockchain, the object is not changed by the signature, enabling you to sign documents in parallel and implement business rules based on mandates, 4-eyes, majority vote, seniority, and others.
- Lastly, but not less important, you can register multiple actions in a sequence on a blockchain. Each registration is linked to a specific case, document, and task performed by the parties involved, creating a chain of transactions: an auditable trail. This audit trail can then be verified by authorized third parties, providing transparency, compliance, and, most importantly, trust.
CB Blockchain Seal for SharePoint
CB Blockchain Seal for SharePoint is the ready-to-use solution for Microsoft SharePoint that allows you to digitally seal the documents you store in SharePoint using blockchain technology.
Adding digital signatures to PDF files or Word documents is probably the most obvious use case, but this solution works with virtually any kind of document or file.
You can prove that no-one tampered with the document the digital signature was added to from a certain moment onwards. The fact that the digital seal is timestamped is essential, for example, to protect intellectual property.
To learn more about this innovative technology, watch a quick demo here: https://youtu.be/HGCbHcN_CK8
Takeaways
- Blockchain is a technology that can assist with the verification of tamper-proof documents.
- Signature and verification are separate processes that do not depend on a central authority.
- CB Blockchain Seal for SharePoint allows us to sign documents and store their seal on a blockchain digital ledger.
Want to learn more? I recommend these articles from our blog:

Stefano Tempesta
Author:
I would love to have your feedback, leave a reply below!

Comments 10
Really Nice article, very impress with the blockchain technology that help to making digital signature secure.
Explained very well on Blockchain and digital signature. Big Thumps up to the article.
Very good information. Can you please elaborate on how to create your digital signatures in blockchain? Thank you
This article discusses CB Blockchain Seal for SharePoint. This product takes care of digitally signing documents, by calculating the hash value of the content, and then storing it on the blockchain. But CB Blockchain Seal is actually a solution you can integrate into other products other than SharePoint. You can also just use this approach online https://www.connecting-software.com/blockchain-seal-verifier/
Thanks for sharing this useful information! Hope that you will continue with the kind of stuff you are doing.
Amazing information about The Future is Now: Digital Signatures move on to Blockchain Technology. Thank you sharing.
Digital signatures stored on a blockchain live independently of the object the signature refers to. There is no need for a central certificate authority or central timestamping server, which are the typical dependencies of existing e-signature systems.
What an exquisite article! Your post is very helpful right now. Thank you for sharing this informative one.
what an exelent article about blockchain, thanks for this information.
What an exquisite article! Your post is very helpful right now. Thank you for sharing this informative one.